Most economic activities often cause damage to the environment and animal agriculture and meat processing industries are no exception. Interaction of these activities with the environment have a huge impact on the ecosystem. Increasing demand for meat production is attributed to the depletion of natural resources and you may be wondering how this is even possible.
Infographic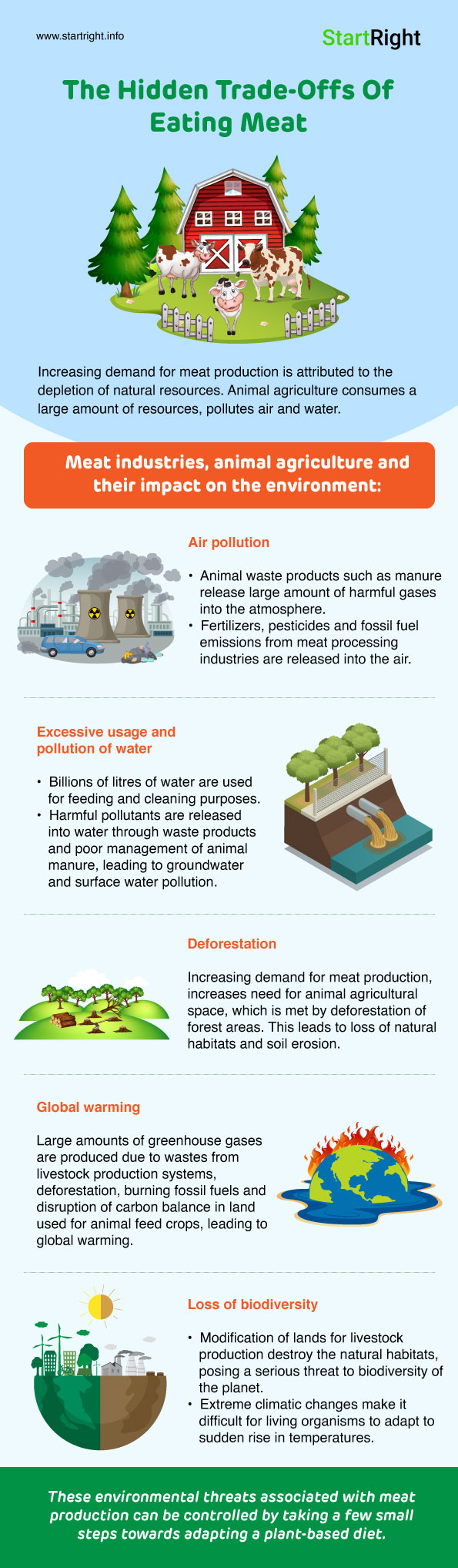 Click Here | Well, it is important for all of us to understand the fact that animal agriculture consumes a more resources, pollutes air and water, leading to a point where humans would not have any natural resources remaining for their own consumption. Quite an alarming situation to imagine, isn’t it? Let us go into a little more depth on how meat industries and animal agriculture are negatively impacting the environment. |
- Air pollution
Animal waste products such as manure release large amount of harmful gases into the atmosphere which include methane, ammonia, nitrous oxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, etc. A number of fertilizers, pesticides and fossil fuel emissions from meat processing industries are released into the air, disturbing the carbon balance which leads to reduced amount of oxygen levels in the air. These air pollutants are carried to long distances by the wind and have the capability to affect areas far away from their point of origin.
- Excessive usage and pollution of water
Livestock production accounts for 8% of the global water usage. This water is mainly used for the growth of feed crops of animals. Billions of litres of water are used each year in animal agriculture for feedings purposes, cleaning of farm wastes, slaughterhouses and improved production leading to water shortages.
Animal agriculture can release harmful pollutants into water through waste products and poor management of animal manure. Harmful pathogens and other substances such as nitrogen, phosphorous can lead to pollution of groundwater and surface water, creating a toxic environment for aquatic life.
- Deforestation
The demand for meat production has been increasingly rapidly. As demand increases the need for animal agricultural space increases. Large areas of uncultivated land are required for livestock production, therefore huge forest areas are cleared out to make space for animal grazing and crop production. This leads to loss of natural habitats for thousands of animal and plant species, eventually causing extinction. Deforestation along with overgrazing results in soil erosion and loss of soil nutrients. It is also one of the key factors associated with global warming.
- Global warming
Wastes from livestock production systems contribute to the release of major greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, water vapour, etc. Large amounts of greenhouse gases are also produced because of deforestation, burning fossil fuels and disruption of carbon balance in the land used for animal feed crops. These greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun and cause rise in temperatures with extreme climatic changes which are difficult to cope with.
- Loss of biodiversity
Modification of lands for livestock production destroy the habitats of specific species within the ecosystem. Extreme climatic changes make it difficult for the living organisms to adapt to sudden rise in temperatures associated with global warming. Ecosystems of the aquatic and terrestrial environments are adversely affected by acidic rains, waste/pathogen discharge on land and freshwater bodies. Invasion and exploitation of resources by livestock themselves pose a serious threat to biodiversity of the planet.
Conclusion:
These are some major environmental threats associated with meat production industries and animal agriculture. The positive takeaway is that these can be controlled by taking a few small steps towards adapting a plant-based diet for a healthier life and a safer planet.
References:
- Livestock and the environment. The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO). United Nations (UN).
http://www.fao.org/3/i0680e/i0680e04.pdf
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Livestock’s role in climate change and air pollution. The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), United Nations (UN).
http://www.fao.org/3/a0701e/a0701e03.pdf
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Water use in livestock production systems and supply chains. The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), United Nations (UN).
http://www.fao.org/3/ca6649en/ca6649en.pdf
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Cattle ranching and deforestation. The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), United Nations (UN).
http://www.fao.org/3/a0262e/a0262e.pdf
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Livestock’s impact on biodiversity. The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), United Nations (UN).
http://www.fao.org/3/a0701e/a0701e05.pdf
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- How livestock farming affects the environment. Down to Earth.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/factsheet/how-livestock-farming-affects-the-environment-64218
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Gowri K, Danielle N. Global Farm Animal Production and Global Warming: Impacting and Mitigating Climate Change. Environmental Health Perspectives (2008); Vol 116:5.
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.
- Edmundo M. Environmental Impact of Livestock Production. J Agricultural Research and Technology (2017); 2471-6774
Accessed on 28 June, 2021.