Balanced maternal nutrition during pregnancy is imperative for the mother’s health status and, consequently, for offspring, and is crucial to maintain an adequate environment for optimal foetal development and also get the mother out of post-partum depression.
Infographic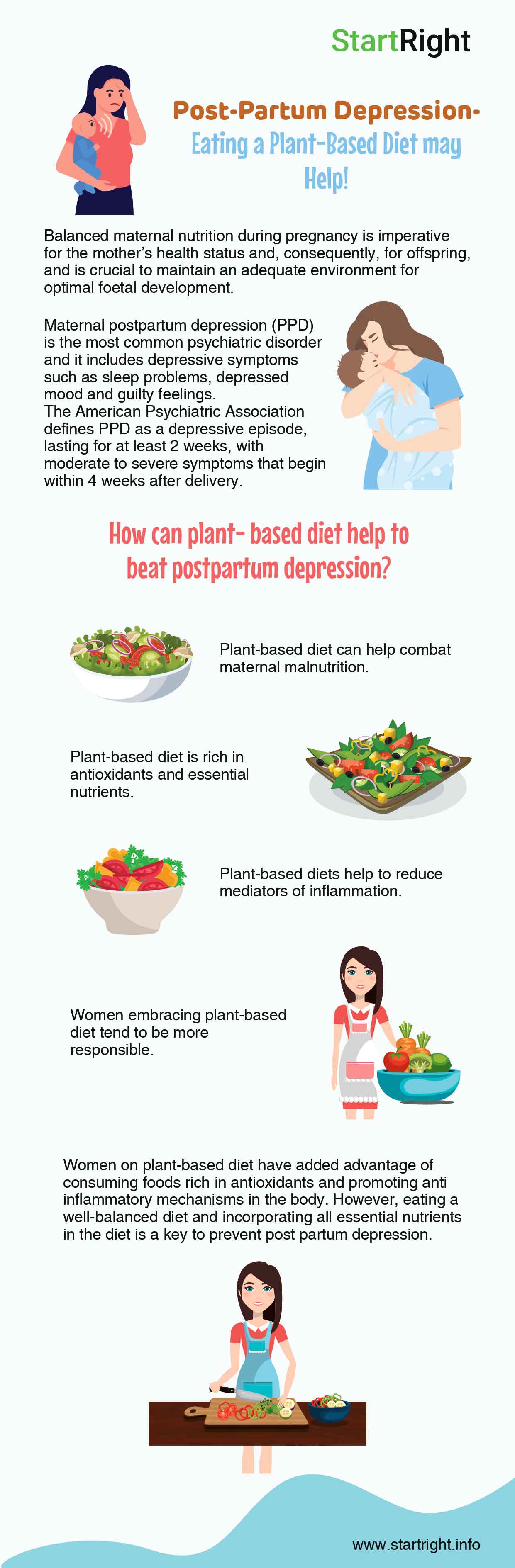 Click Here | According to the American Dietetic Association, well planned plant-based diets are safe for all age groups and in all physiological conditions, including childhood, adolescence, pregnancy, and lactation. However, the decision to adhere to a plant-based diet during pregnancy may also benefit in many other ways to the mother and the child. Previous studies have indicated that dietary patterns during pregnancy have a varied effect on maternal health and pregnancy outcomes such as hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP), gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), preterm birth and low birth weight. Plant-based diets are reported to contain less saturated fatty acids, animal protein and cholesterol, and more folate, fibre, antioxidants, phytochemicals, and carotenoids. |
Another arising negative outcome pf pregnancy is post-partum depression. Maternal postpartum depression (PPD) is the most common psychiatric disorder and it includes depressive symptoms such as sleep problems, depressed mood and guilty feelings.
The American Psychiatric Association defines PPD as a depressive episode, lasting for at least 2 weeks, with moderate to severe symptoms that begin within 4 weeks after delivery. However, literature has indicated that depressive episodes after childbirth are more likely to occur even outside the first 4 weeks compared to non-childbearing periods; specifically, such depressive episodes after childbirth can be frequently observed for 3–6 months postpartum.
Many of us have heard the term ‘post partum blues ‘. This broadly refers to mild mood disturbances that occur within first week of post partum period. However, this is a temporary phase and the ‘blues ‘ usually disappear within days; however, in some women, they can be aggravated and become PPD.
How can plant- based diet help to beat postpartum depression?
1) Plant-based diet can help combat maternal malnutrition.
Maternal malnutrition combined with socio-economic and environmental factors can make some women susceptible to post partum depression.
Specific nutrients are needed in greater quantities during pregnancy and postpartum, and deficiencies in these nutrients may increase the risk of postpartum depression.
Intake of vegetables, fruits and legumes improves micronutrient and antioxidant intakes, which could improve pregnancy and birth outcomes, particularly at the second trimester, since oxidative stress has been shown to reach high levels mid-pregnancy.
2) Plant-based diet is rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients.
The role of nutrition in maternal mental health may not be as well understood as other facets of wellness, however recent studies suggest that certain nutrient deficiencies may increase the risk of postpartum depression. Trace minerals, including selenium, zinc, iron, vitamin D, vitamin B complex and essential fatty-acids such as EPA/DHA play an important role in nutrition of the mother.
Research shows that certain hormonal changes and low levels of some hormones like oxytocin, calcium, tryptophan, and monoamine oxidase may precipitate PPD in susceptible women.
Plant-based diet has been shown to be rich in antioxidants which help to combat stress. These diets include vegetables, fruits, seeds, nuts and vegetable oils which are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids. An open trial demonstrated that levels of depression were reduced with supplementation of EFA and DHA, two omega-3 fatty acids.
3) Plant-based diets help to reduce mediators of inflammation.
The inflammation hypothesis is supported by many studies that found raised levels of pro-inflammatory chemicals in depressed patients. A plant-based diet had been proven to reduce chronic inflammatory mediators in the long run. Hence, mothers consuming plant-based diet can benefit from this.
4) Women embracing plant-based diet tend to be more responsible.
Women consuming plant-based diets have opted for this dietary pattern based on ethical and environmental choices. They tend to be more mature and likely to accept the challenges of pregnancy with an open mind.
To summarize, women on plant-based diet have added advantage of consuming foods rich in antioxidants and promoting anti inflammatory mechanisms in the body. However, eating a well-balanced diet and incorporating all essential nutrients in the diet is a key to prevent post partum depression.
References:
- An open trial of Omega-3 fatty acids for depression in pregnancy.
- Sona-SanaeAoyag, Kenji J. Tsuchiya Does maternal postpartum depression affect children’s developmental outcomes?J Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 45, No. 9: 1809–1820, September 2019.
- https://www.eatlivelovefood.com/postpartum-depression/