Fats are an integral part of our dietary requirements, and as per recommendations, 20% of our diet should contain fats. They not only provide our bodies with energy but also help it to absorb vital nutrients and produce hormones. It is, therefore, crucial to understand the difference between various types of fats, their role in our body, and how to choose good fats over bad ones.
Saturated Fats
Fats containing no double bond in their chemical structures are known as saturated fats. These fats are solid at room temperature, therefore, also known as ‘solid fats.’ Animal products are enriched with these kinds of fats such as chicken, pork, and beef.
Some of the most commonly used foods that contain an excessive amount of saturated fats include:
- Baked foods including; donuts, croissants, cakes, pastries, and cookies
- Cheese containing foods, for example, burgers and pizza
- Hot dogs, ribs, and sausages
- Dairy products including ice cream
- Fried potatoes, cooked in saturated fats or trans oils
- Processed foods
Trans Fats
Trans fats are the derivatives of vegetable oils, which are made by the process of hydrogenation. Animal products are rich in trans fats, for example, whole milk and animal meat. They are also used in many bakery products, such as cakes, icings, cookies, and popcorns. Trans fats also raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases; therefore, they must not be consumed in daily diet.
This type can be further divided into two categories : naturally-occurring trans fats and artificial trans fats. In modern culture, all processed food items, such as cakes, pizza, cookies, and margarine, use artificial trans fats.
Unsaturated Fats
Fats containing one or more double bonds are unsaturated fats. They tend to be solid at room temperature, yet many of them are also liquid, for example, vegetable oils. Unsaturated fats are ‘good fats’ as they fulfill our body’s nutritional requirements.
Polyunsaturated fats and monounsaturated fats are the types of unsaturated foods. Both these types help lower your LDL cholesterol, in turn reducing the risk of heart-related diseases.
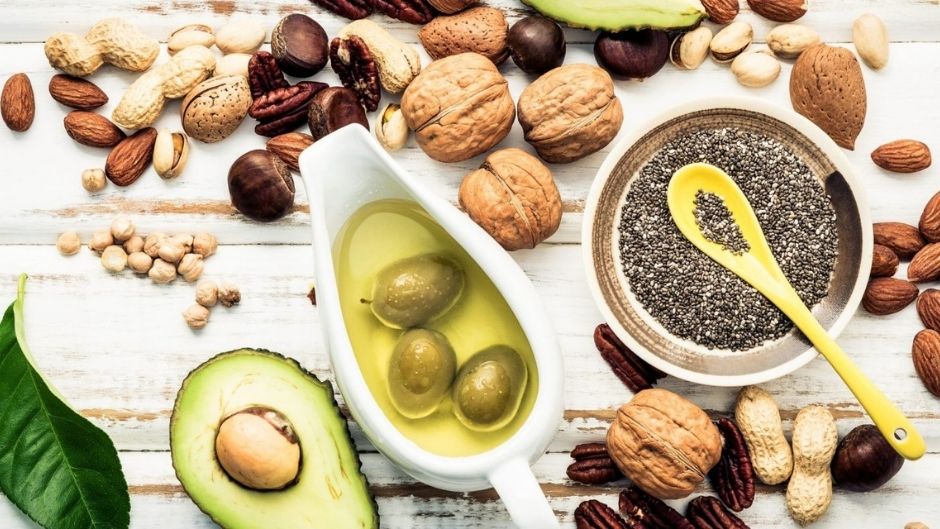
Plant-Based Whole Foods – Perfect Source of Good Fats
Fats from plants are far better for your health as compared to fats derived from animals. The reason behind this superiority is the dominance of unsaturated fats in fats over unsaturated ones. Plant-based foods contain only a minute amount of saturated fats. The majority of their nutritional content consists of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
The minute amount of saturated fats that are present within the plant-based foods is also acceptable. According to the U.S National Library of Medicine, 16 to 22 grams of saturated fats are acceptable each day.
According to a recent experiment conducted by Harvard research institute, people eating plant-based fats have reduced the risk of causalities by 16%; however, consumption of animal-derived fats increases the chances of death by 21%. This fact alone should make you switch to plant-based fats.
The following are certain plant-based foods that are rich in essential unsaturated fats and oil.
- Avocado
A green fruit that comprises a sufficient amount of saturated fats, more than 77% of its calories come from fats. Avocadoes are enriched with oleic acid, a monounsaturated fatty acid, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Flaxseeds
Also known as linseeds or common flax is a terrific source of plant-derived omega-3 fatty acid, alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). This ALA is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid that is required by the body in the diet as the body cannot synthesize it by itself. It also protects the body from health-related issues.
- Hemp Seeds
Seeds derived from Hemp plants are known as hemp seeds. They contain two essential plant-based polyunsaturated fatty acids, namely omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. They reduce the chances of cardiovascular diseases, skin-related disorders, and premenstrual syndrome.
- Peanuts
Dry fruit that contains more than 50% of the unsaturated fats (both mono and polyunsaturated fats). All of the encompassed fats reduces the risk of heart disorders and also reduces the LDL cholesterol level in the human body.
- Walnuts
They are composed of “good fats” as they are the perfect source of omega-3 fatty acids as they contain omega-3 more than any other nuts found on Earth. Eating walnuts provide you with essential fatty acids that are required to minimize oxidative stress, as well as inflammation within the brain and therefore, support the brain in performing its daily-based activities.
- Sesame Seeds
Seeds of sesame plants are composed of 80% saturated fatty acids. Recent experimentation depicted that eating sesame seeds can lower down the body LDL cholesterol level as well as triglycerides. They also act as good anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory agents to lower down the risk of the heart linked health complications.
- Plant-Based Oils
Plant-derived oils are composed of significant amounts of essential fatty acids. These are obtained from different plants, for example, soybeans, corn, olives, peanuts, and sunflowers. Some of these oils are unsaturated, while others are saturated in nature.
You should prevent yourself from eating oils containing saturated fats and prefer oils containing unsaturated fats. Examples of plant oils containing saturated fats are palm oil, palm kernel oil, and coconut oil, while canola oil and olive oil consist of unsaturated fats.
Conclusion
It is a popular myth that fats must be prohibited from your daily diet plan, as all of them have hazardous effects on the human body. However, your body needs fats for proper functioning and maintaining its temperature within the acceptable range.
Saturated fats are the ones that are categorized as bad fats, whereas unsaturated fats are the “good fats” that are required by the human body. Plant-based foods are full of unsaturated fats; hence, they should be preferred over animal-based foods, which are a rich source of saturated fats.