Breast milk is brimming with nourishment and protective compounds that are essential for your baby’s development. Except for vitamin D, breast milk contains everything your baby needs for proper development during the first 6 months. Therefore, breast milk is frequently referred to as the gold standard for infant nutrition.
Infographic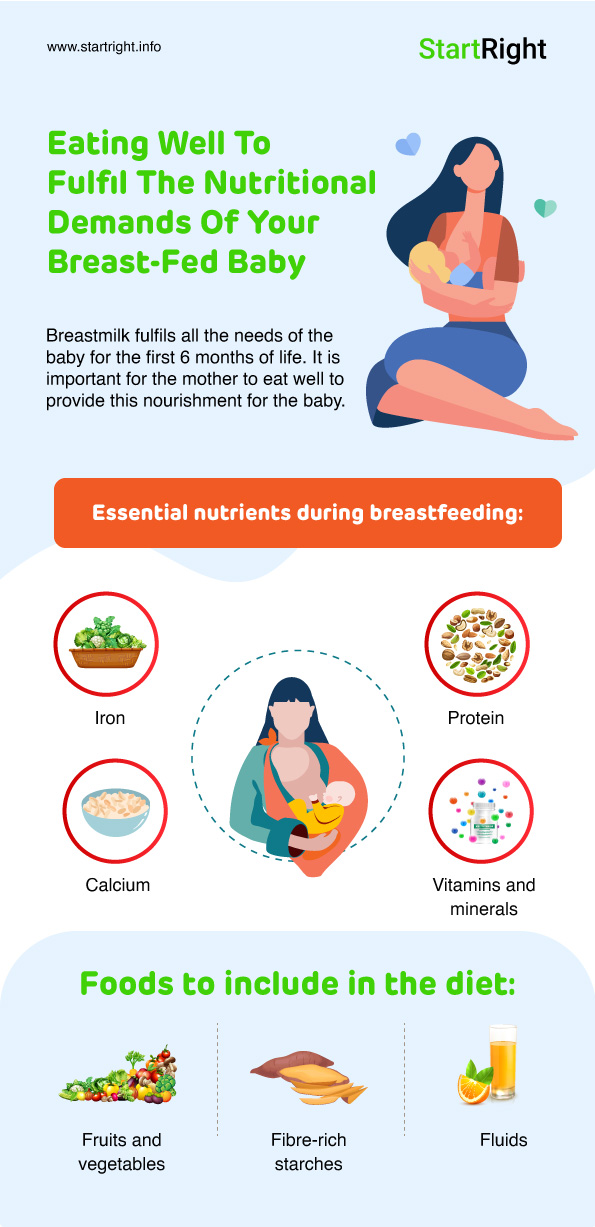 Click Here | After delivery, it is common for women to be deficient in vitamins and minerals. But if your overall diet does not provide sufficient nutrients, it can affect both the quality of your breast milk and your own health. A plant-based diet can meet the nutritional needs of a breastfeeding mother as long as it includes a wide range of nutrient dense foods. |
It is important to choose foods that are rich in iron, protein and calcium and of course vitamins and minerals
Iron:
Good sources of iron include lentils, beans, enriched whole grain cereals, leafy greens, and dried fruit, like dates, apricots and raisins. To help your body in absorption of iron, consume foods rich in vitamin C such as citrus fruits, guava, papaya, etc.
Protein:
On a plant-based diet, it becomes very necessary to ensure you are consuming adequate protein. Sources like soy products, meat substitutes, legumes, lentils, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are a good start. Try to include protein in at least two meals every day.
Calcium:
The milk you produce can deplete your calcium stores if not replenished frequently. Some good sources of plant-based calcium are dark green vegetables, cereals and soy products.
Fruits and vegetables:
Varying your fruit and vegetable intake can give you a wide range of nutrients. Pick brightly coloured fruits and veggies to obtain maximum benefit. Eat at least 2-3 servings of both fruits and vegetables daily.
Fibre-rich starches:
To feel satiated and keep your gut flora and immune system in good health, it is vital that you consume fibre rich foods. Try to include potatoes, butternut squash, sweet potatoes, beans, lentils, quinoa, and whole grains such as whole wheat breads, pasta, cereal, brown rich, ragi and oatmeal in your daily diet.
Multivitamins
Consider taking a multivitamin or nutritional supplements. Typically, your doctor will recommend a daily vitamin B-12 supplement. This is because in nature, vitamin B-12 is almost exclusively found in animal products, and it can be difficult to get enough from a plant-based diet alone. Omega-3 and vitamin D supplements may also prove helpful to you.
Not just you, but your baby may also need a vitamin D supplement to absorb calcium and phosphorus. However, before you begin any supplements for your baby, it advisable to speak to your doctor about it.
Occasionally, a mother’s calorie or fluid intake can affect milk production. Your body’s requirements change during breastfeeding, it is best to take this into account when planning your meals.
Calorie intake:
Typically, your body will require an additional 300 to 500 calories while breastfeeding. Listen to your body and eat when your appetite strikes, you do not need to count calories during this phase. Eat sensible nutritious food and avoid alcohol and caffeine. Do not try extreme diets to lose pregnancy weight, because this can reduce your milk supply and harm your baby.
Fluid intake:
As a rule of thumb, drink to satisfy your thirst. It is not necessary to force yourself to drink too much water. As a natural response to breastfeeding, your body will release the hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin through natural biological processes stimulates a sensation of thirst. This mechanism usually ensure that you drink enough water to meet your new fluid needs.
Conclusion:
Breastfeeding is a phase where you need to pay more attention to the nutrients you are receiving, as your baby receives the nutrients through your breastmilk. Make sure you eat foods that are rich in the above-mentioned nutrient, have enough water and fluids, and take the prescribed multivitamins. This will ensure that you and your baby have a healthy life.
References:
Breastfeeding and your diet. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/HealthyLiving/breastfeeding-and-your-diet.
Accessed on 28-06-2021
Eat Healthy While Breastfeeding: Quick tips. Health.
https://health.gov/myhealthfinder/topics/pregnancy/nutrition-and-physical-activity/eat-healthy-while-breastfeeding-quick-tips.
Accessed on 28-06-2021
Breast-feeding nutrition: Tips for moms. Mayo Clinic.
https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/infant-and-toddler-health/in-depth/breastfeeding-nutrition/art-20046912.
Accessed on 28-06-2021