In 2018, an estimated 69 billion chickens, 1.5 billion pigs, 656 million turkeys, 574 million sheep, 479 million goats, and 302 million cattle were slaughtered for meat production! These figures are appalling and are a robust proof of our cruelty towards animals. By farming animals and killing them for food, despite availability of better plant-based options, shows our selfishness, and unfairness in sharing the Mother Earth with all.
Though we cannot change the scenario overnight, at least we can start eating healthy by adopting a plant-based, whole-food diet. Keep reading to know how our transition to a plant-based diet changes the whole ecosystem.
Meat on your plate may have dire environmental consequences
In addition to being the major drivers of top human killer diseases, such as obesity and heart disease, animal products are also the major contributor to climate change, animal suffering, land consumption, water pollution, and the burning of fossil fuel, which gradually harm the environment. Switching to a plant-based diet could be a win-win for humans, society, and the environment.
Infographic Click Here | A plant-based diet focuses on foods rich in fruits, vegetables, beans, peas, or nutrients obtained from plants while minimizing or completely eliminating processed foods, oils, and animal foods, including dairy products and eggs. |
Animal-based food: A threat to our ecosystem
There are more than one ways that our environment is affected when we as a population eat animal-based foods. When we eat animal-based foods, we:
- Increase greenhouse emissions
According to The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the production of livestock releases 14.5% of global greenhouse gas. On the other hand, the production of plant-based foods doesn’t emit much greenhouse gas than animal-based products. It is also found that if we avoid red and processed meat, we could reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 27.8 million tonnes per year.
The production of plant-based foods requires less land, water, energy and doesn’t have much destructive effects on the environment.
- Increase the consumption of fossil fuels
Fossil fuels are getting depleted everyday and we use these fossil fuels in different processes involved in producing animal food. If estimates are to be believed, producing 1 kcal of animal protein requires energy input from fossils that are 11 times higher than what is required in the production of same amount of grain protein. Do we need a stronger reason to quit animal-based food?
- Deplete our water-resources
According to studies, animal-based food products require twice the amount of water as plant-based foods of the same weight. However, the amount of water changes with the type of animal and production system.
The production of 1kg beef requires over 20 times more water compared to the production of rice, grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables; 800 litres of water is needed for the production of one litre cow’s milk i.e., four times the production of one litre soy milk; 43% of irrigation water is required for raising animals for food whereas plants require only 24% of irrigation water. If this scenario continues then the world will run out of the water by 2050.
In addition to water scarcity, the production of animal-based foods is the major contributor of freshwater pollution.
- Destroy our forests
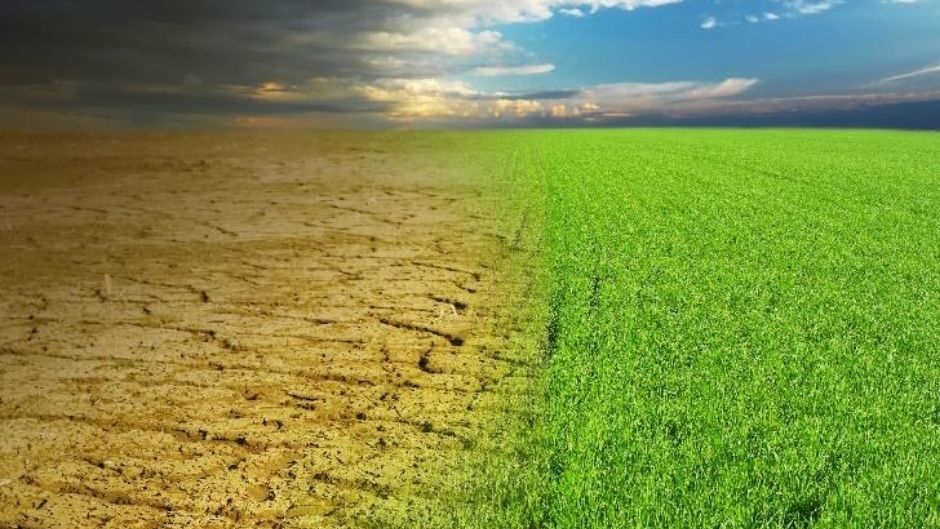
Animal agriculture has become one of the most important reasons behind deforestation. Globally, we destroy a third of arable land to raise animals, such as pigs, cattle, and chicken for food. This destruction has also contributed to the extinction of species, such as orangutans, red pandas, and sloths.
According to research, animal agriculture requires 17 times more land than plant-based agriculture. If everyone throughout the world adopts a plant-based diet then the destruction of farmland will drop by 75%.
From the impact on human health to the whole planet plant-based diet offers several benefits. Also, with a plant-based diet, the demand for meat, dairy products, and egg get reduced, which drastically reduces animal abuse and cruelty in animal farms. There are no big secrets in a plant-based diet, you just need to set a goal of eating mostly plant-based foods. If you are having 21 meals a week then go for 15 plant-based meals. These small steps gradually will have a huge impact on your health and the planet.
References:
- Tuso PJ, Ismail MH, Ha BP, Bartolotto C. Nutritional update for physicians: plant-based diets. Perm J. 2013;17(2):61-66.
- Lynch H, Johnston C, Wharton C. Plant-Based Diets: Considerations for Environmental Impact, Protein Quality, and Exercise Performance. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1841.