Dietary fats are the type of oils and fats that occur naturally in plants and animals-based foods. Dietary fats mainly consist of fatty acids.
These dietary fats make an essential constituent in our diet plan as they provide energy to our body and also facilitates cell growth, apoptosis, and necrosis. Fats also play an essential role in absorbing nutrients, protecting body organs, and also maintain body temperature within an acceptable range. They also support brain functions; therefore, fats are an essential part of our diet.
Types of Fats
Broadly fats are divided into three major types, including saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats, where saturated and trans fats fall in the bad fats category as they impart a very harmful effect on human health.
All these types have varying physical and chemical properties. For example, unsaturated fats are mostly liquids in nature, such as vegetable oils, while saturated and trans fats are solid at room temperature. Saturated fats are deprived of double bonds within their structures, while one or more double bonds are available in unsaturated fats.
If there is only one double bond present in the chemical structure of fats, then they are termed monounsaturated. Whereas; polyunsaturated fats are those, which have more than one double bond.
How Fats Affect Our Body?
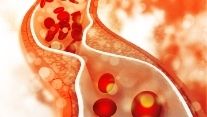
Fats impart diverse effects on the body’s cholesterol levels. The bad fats are responsible for increasing the levels of Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and chances of cardiovascular disorders. Contrary to this, saturated fats not only lessen the LDL cholesterol but also impart positive effects on the body.
Side Effects of Bad Fats
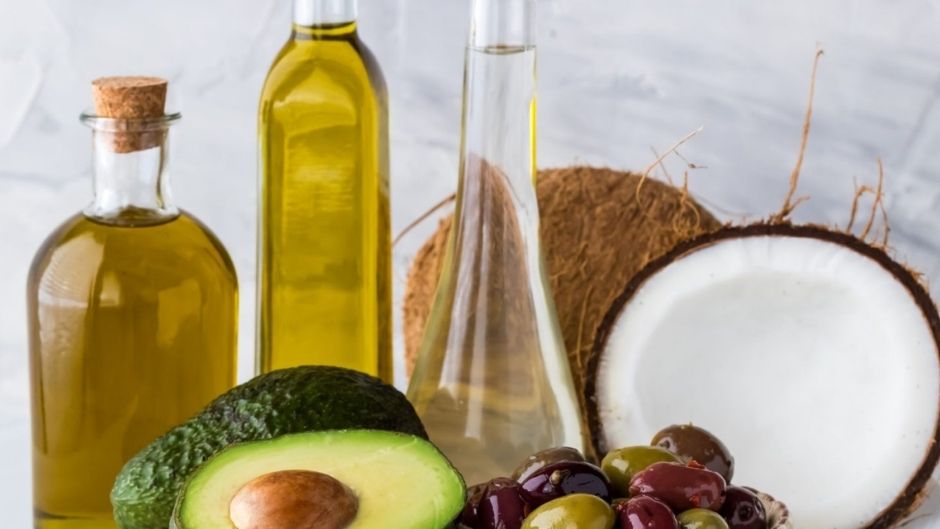
Side-effects of unsaturated fats and trans fats dominate over their health benefits; therefore, fat-rich foods should be avoided as much as possible. Chicken fats, beef fats, pork fats, butter, cream, and margarine are the few examples of foods which are enriched in bad fats, whereas plant-derived foods are full of saturated fatty acids; hence these foods must be taken in daily diet to meet the body requirements of fats and oils. Common examples of plant-based foods that are full of saturated fats include coconut oil, palm oil, and other vegetable oils.
Plant -based fats are nature’s perfect gift, and sources of plant-based fats with their health benefits.