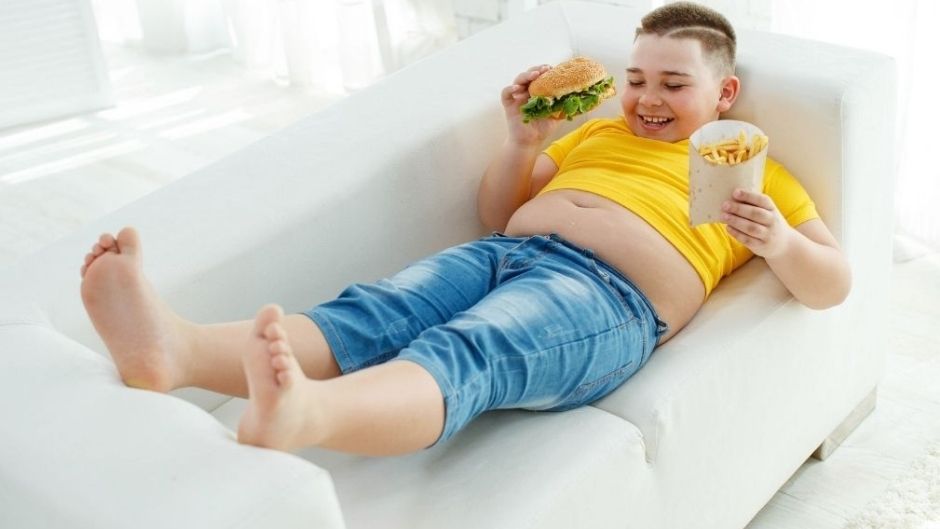
Childhood obesity is a worldwide concern. Dramatic increases are occurring in urbanized areas of developing countries. In light of the consensus that childhood obesity is a significant public health concern, there has been extensive research over exploration of food eating patterns of this population.
Infographic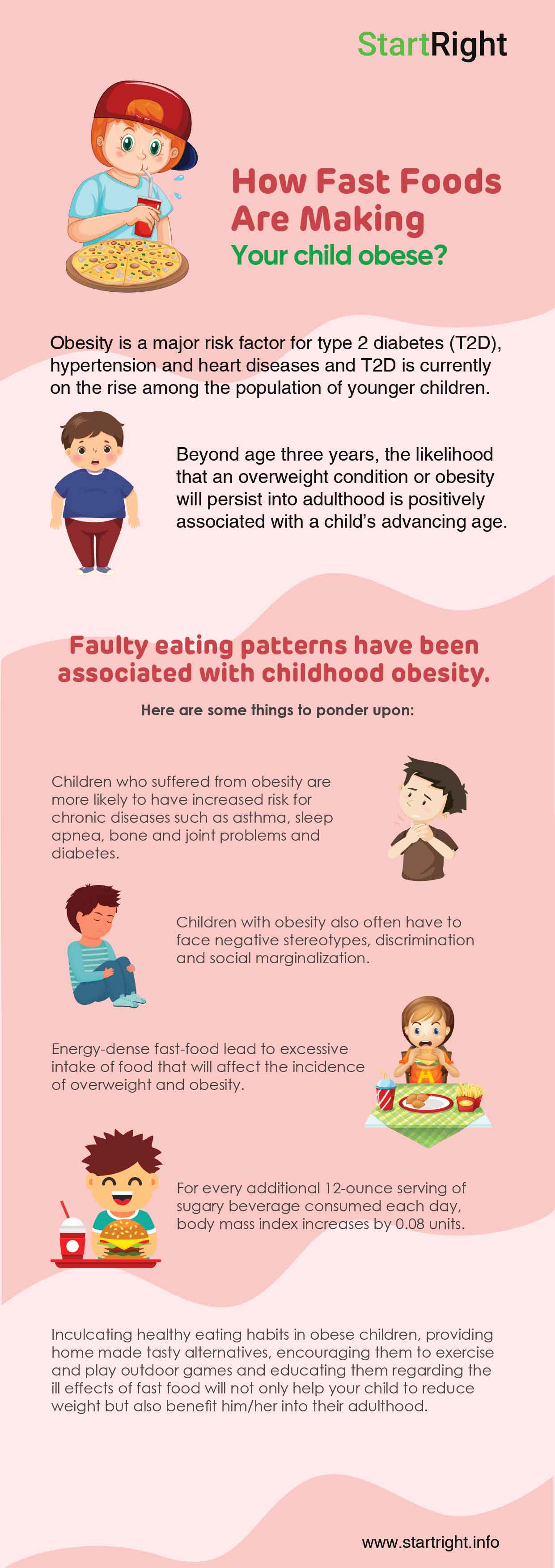 Click Here | Overweight status during childhood has negative health consequences during childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes (T2D), hypertension and heart diseases and T2D is currently on the rise among the population of younger children. Beyond age three years, the likelihood that an overweight condition or obesity will persist into adulthood is positively associated with a child’s advancing age. Once an obese child reaches age of six, there is a 50% probability that obesity will persist. Of greatest concern is that 70–80% of obese adolescents will remain obese as adults. |
Faulty eating patterns have been associated with childhood obesity. So, if your child is gaining weight and has habit of eating fast food, here are some things to ponder upon:
- Children who suffered from obesity are more likely to have increased risk for chronic diseases such as asthma, sleep apnea, bone and joint problems and diabetes.
- Children with obesity also often have to face negative stereotypes, discrimination and social marginalization compared with peers who have normal weight, experience bullying, and have lower self-esteem. In addition, they also suffer from psychological problems such as anxiety and even depression.
- Energy-dense fast food include biscuits, cakes, pudding, pastels, fruit syrups, chocolate flavoured drinks, isotonic drinks, fruit juices, flavoured drinks, soft drinks, ice shakes, chocolate, candy, sweetened condensed milk, milkshakes, ice cream, milk, fried foods, sausages, potato chips, crackers, snack bar, fried nuts, popcorn, white sugar, sauce and toppings. Research suggests that consumption of high energy density foods lead to excessive intake of food that will affect the incidence of overweight and obesity. Such foods usually contain low protein and provide empty calories.
- Fast foods such as salted potato chips, wafers, chocolates, and candies have high sodium, sugar, and saturated fat content. Restaurants, food joints, food trucks selling fried chicken, burger, hotdog, sandwich, and pizzas are loaded with fats and sodium. In addition, preservatives, artificial sweeteners, and artificial food colours are incorporated which possess risk to health.
- Fast food is favoured by children because of the characteristics that are practical, delicious, and satiating. The delicious flavour caused by increased primordial palatability due to the high sugar, fat, and salt content. Another characteristics of fast food is, it tends to have high energy density, saturated fat content and high trans fats, low fiber content and micronutrients, high glycemic load, and huge portions.
- A systematic review and meta-analysis of 88 studies found “clear associations of soft drink intake with increased caloric intake and body weight.” In children and adolescents, a more recent meta-analysis estimates that for every additional 12-ounce serving of sugary beverage consumed each day, body mass index increases by 0.08 units.
- Another recent survey conducted among school children concluded that students who consumed fast food >3 times/week were 2.42 times more likely to be overweight and obese compared to students who consumed fast food ≤3 times/week.
- It is known that a balanced diet can help contribute to maintaining a healthy weight. Eliminating sugary beverages and snack foods, which both contribute to a higher caloric intake, can help to decrease the risk of childhood obesity (Sahoo et al., 2015).
Inculcating healthy eating habits in obese children, providing home made tasty alternatives, encouraging them to exercise and play outdoor games and educating them regarding the ill effects of fast food will not only help your child to reduce weight but also benefit him/her into their adulthood.
References:
Rosenheck R. 2008. Fast food consumption and increased caloric intake: a systematic review of a trajectory towards weight gain and obesity risk. Obes Rev 9(6):535-547.
Sahoo, K., Sahoo, B., Choudhury, A. K., Sofi, N. Y., Kumar, R., &Bhadoria A. S. (2015). Childhood obesity: causes and consequences. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 4(2), 187-192. Doi 10.4103/2249-4863.154628.
Nisak AJ, Rachmah Q, Mahmudiono T, Segalita C (2018) Snacking Energy-dense Food Related to Childhood Obesity. J Nutr Food Sci 8: 725. doi: 10.4172/2155-9600.1000725